Extend Partition by using Windows disk management.
To expand/extend system boot partition and increase its free space in Windows 2000, Windows XP and Windows 2003 is very difficult to do in the past time, because their built-in Disk Management did not provide the functions of extending partition or shrinking partition, this would have to use third-party tools such as Partition Magic, Disk Director, and other partition management software to accomplish the extending volume operation.However, in Windows Vista, Windows Server 2008 and Windows 7 times, Expanding Volume is no longer a difficult task, because Disk Management of Vista, Win2008 and Win7 have been built in the functions such as expanding volume and shrinking volume, and also include extending system partition, which is very easy to use without relying on 3rd party partition utilities. It's able to extend primary partition and logical partition, at the same time, this feature can not only resize (adjust) the size of a basic partition on a basic disk, but it can also resize dynamic system volume on a dynamic disk. Yet partition magic and other disk management tools can not handle dynamic disks. Thus, resizing a dynamic disk volume is indeed a good feature on Vista, Windows 7 and Windows Server 2008. Now come to experience!
1. Launch windows disk management to extend C: drive
Click Start Menu -> Control Panel -> System and Maintenance -> Administrative Tools -> Double Click Computer Management -> Storage -> Disk Management. Or directly type "diskmgmt.msc" to Start Menu -> Run. It showed below.
2. Extend Volume greyed out in disk management, what can we do?
Then right-click the system boot volume (C:) you want to expand, but you will find "Extend Volume ..." is a grayed out and unusable state, how is this going on, can not be extended? The screenshot is as follows:
3. Generate a contiguous unallocated disk space to extend system partition
How to generate a next contiguous unallocated space here? The method is to reduce D: drive (shrink volume D :) at first, then in the extra unallocated space to create a new partition. Here copy all data of D: drive to the newly created partition and delete D: drive, so that the system partition can be enlarged to the "contiguous unallocated space", follow these steps:- Shrink volume DATA (D:) from 230GB to 120GB as follows:
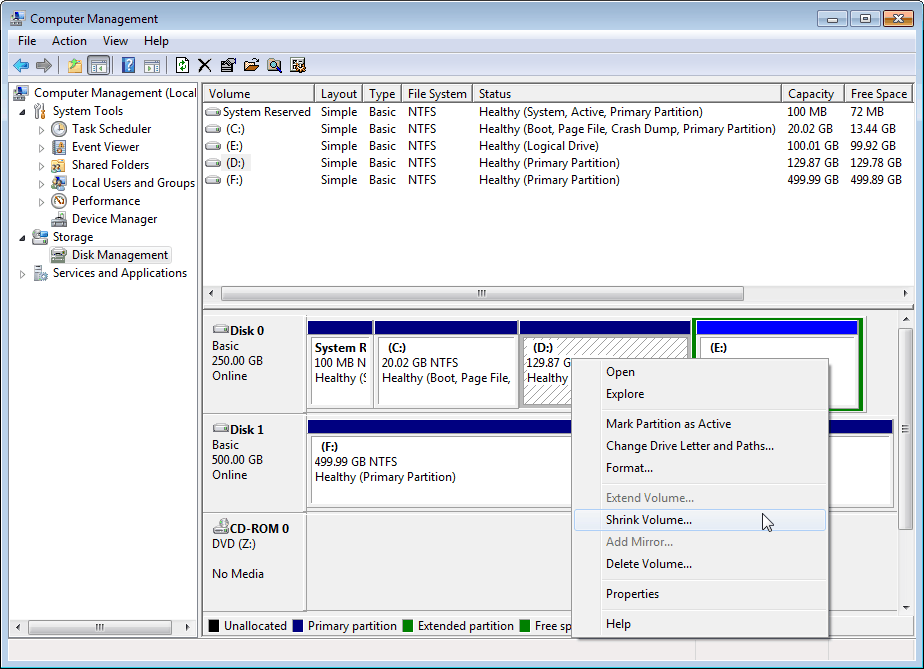
- After clicking "Shrink Volume…" option, the following screenshot is opened:

- Click the Shrink button to confirm, then the disk will generate an unallocated space of 110GB as follows:

- Now you can create a new partition in the unallocated of 110GB, then copy the files of (D:) to the (E:) partition, the following is newly partition (E:)

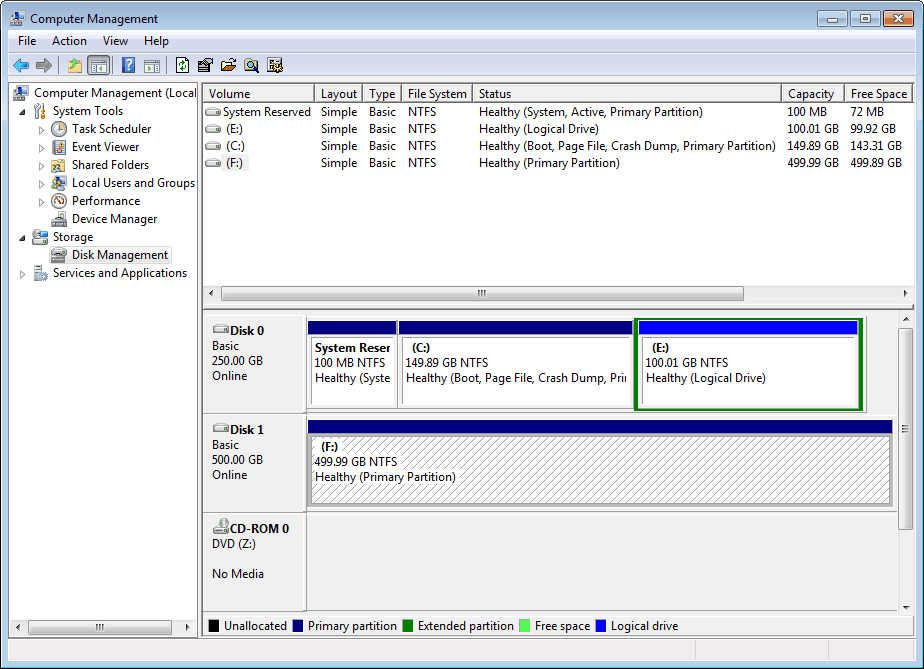
And then, delete (D:) to release 120GB of unallocated space to extend system boot partition (C:).
Please try to Extend Partition Professional Edition of Partition Assistant to directly extend your system partition if a congiguous unallocated space can not be generated.
4. Extending system boot partition
After deleting (D:) partition, it is recommended to change drive letter from E: to D:, thus maintaining the drive letter is the same as before. Now you can extend system partition from 20GB to140GB. In this following screenshot, Windows Disk Management is certainly able to extend or resize system partition by using the contiguous unallocated disk space:
5. Extending partition volume by using the command line
Extending a partition or volume can be done via DiskPart.exe, or command line interface. This works can be done in both Vista, Windows Server 2008 and Windows 7. Start with the following steps:
- Click Start and type CMD, then press Enter.
- In the command prompt type DISKPART.exe
- Select the right hard disk and partition to work on. Typically this should be disk 0 and partition 1. SELECT disk 0SELECT partition 1
Note: You may want to execute a "LIST" command to view your existing disks and partitions before attempting to expand volume. Needless to say, if you don't have any space you can use on the same disk, you will not be able to extend the partition any further. So no real harm can be done here.LIST diskLIST partition
- When the right disk and partition were selected, execute the "EXTEND" command. If you don't specify the size to extend by, then the command will extend the partition by using all of the contiguous space available on that disk. EXTENDThe above command will enlarge the partition by using all of the contiguous space available on that disk.
EXTEND size=2048The above command will enlarge the partition by 2048MB (increase 2GB free space to the partition that you were selected).
6. Expanding system partition from my experience
1). There must be contiguous unallocated disk space after the partition that you want to extend. If haven't a contiguous unallocated space you can directly use Extend partition Professional Edition of Partition Assistant to realize the expansion.2). For extending dynamic system volume on a dynamic disc, its method of operation is exactly the same as the above extending basic disk.
3). When no contiguous unallocated space, there are two ways of creating a contiguous space to extend system boot partition.
- A. The easier way: Copy all data and files in D: drive to an USB hard disk (or other external disks), right-click D: drive and click "Delete Volume…" to generate a contiguous unallocated space.
- B. Troublesome way: Shrink the D: drive partition to create new partition (e.g. E: drive), move D: drive data and files to E: drive, and apply "Delete Volume…" in D: drive.
5). Windows 2000/XP/2003 Disk Management does not support for extending partition and shrinking partition, only the Vista/2008 and Win7 are able to extend volume and shrink volume in the basic disk and the dynamic disk.
6). On dynamic disk of Windows 2000/XP/2003/2008/Vista and Windows 7, it is possible to extend volume to another disk space by using "Spanned Volume" function, but this feature does not support for extending system partition.
7). Common partition software such as Partition Magic, Disk Director, Partition Manager, Partition Master and Partition Wizard support basic disks and does not support dynamic disks.
No comments:
Post a Comment